Hong Kong
Hong Kong Job market
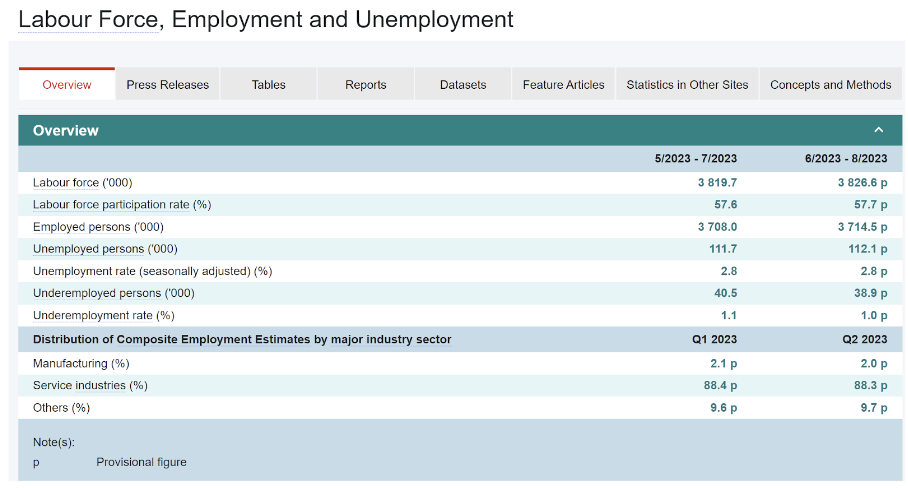
According to the latest labour force statistics (i.e. provisional figures for August – October 2023) released today (November 16) by the Census and Statistics Department (C&SD), the seasonally adjusted unemployment rate increased from 2.8% in July – September 2023 to 2.9% in August – October 2023. The underemployment rate remained unchanged at 1.0% in the two periods.
Source: Census and Statistics Department

Engineering = Innovation x Entrepreneurship
On January 30, 2024, the College’s Bright Future Engineering Talent Hub at City University of Hong Kong organized a Career Exploration Program, which was attended by approximately 60 secondary school students. Additionally, on the same day, the College of Engineering and the College of Science jointly organized Engineering and Science 2024, attracting participation from around 70 companies.
The program covered the following topics:
- Career Planning and Career Opportunities in Hong Kong and neighboring areas.
- AI workshop.
- Experiential learning: Junior Reporters.
During the program, secondary school students were divided into teams of 3 or 4 and assigned the role of junior reporters. Their task was to interview a specific company in order to gain insights into various industries, required job skills, and personal interests. This experience allowed the students to acquire a wealth of knowledge about the industry and discover their own interests along the way.
October 2023 Hong Kong Report
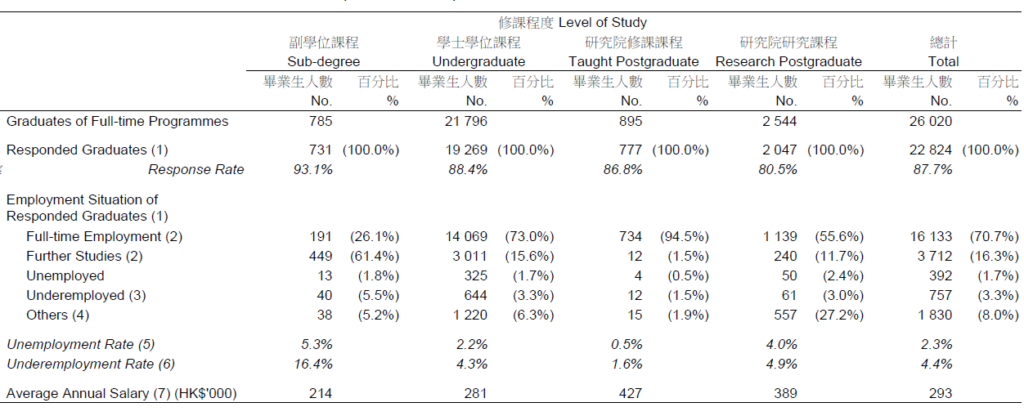
1. Employment Situation of Graduates of Full-time UGC-funded Programmes by Level of Study, 2021/22 (as at 31.12.2022)
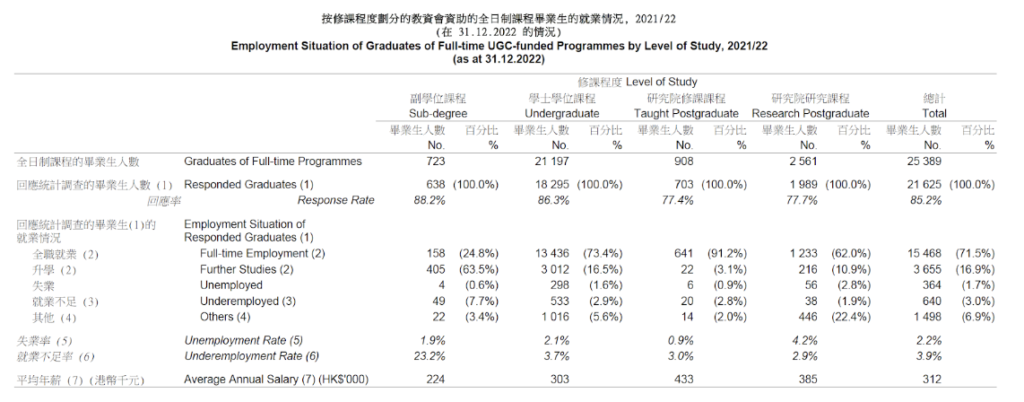
2. Unemployment rate: 2.8%

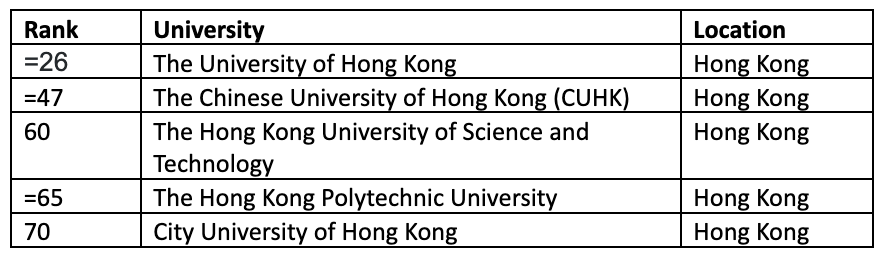
3. Top 100 Universities in the World (According to the QS World University Rankings 2024)
4. Career Planning Workshop for Secondary School Students

July 2023 Hong Kong Report
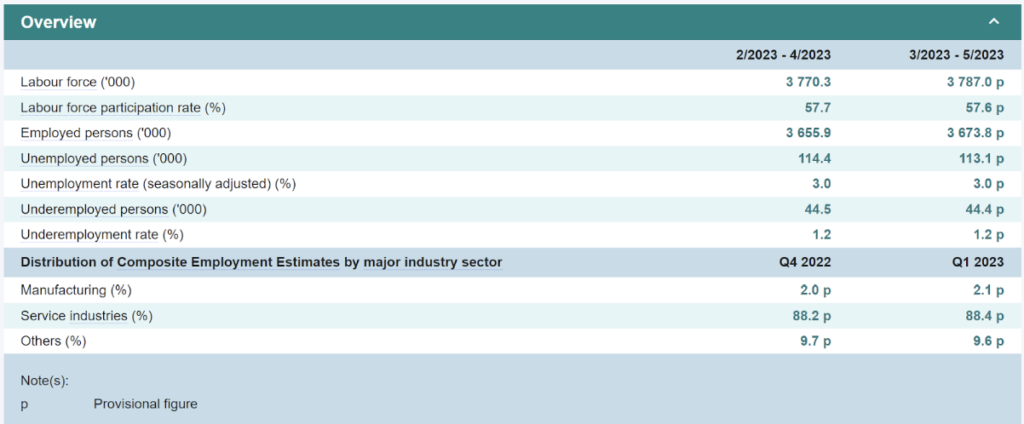
A. Labour Force, Employment and Unemployment
Hong Kong’s unemployment rate drops to 3.0%
B. Hong Kong’s talent attraction scheme
To attract more high-quality talent to come and meeting Hong Kong’s development needs.
- Advice on work visa applications, employment and tax issues
- Advice on housing, co-working spaces, healthcare, education, and social networking in Hong Kong
- Recommendations for suitable career opportunities and talent-matching with recruitment specialists
- Advice on acquiring support from HKSAR government funding schemes
- Assistance with identifying appropriate incubation and acceleration programmes
- Talent List Hong Kong
- Healthcare Services
- Development and Construction
- Innovation and Technology
- Financial Services
- Maritime Services
- Maritime Services
- Creative Industries, Arts and Culture, Performing Arts
- Legal and Dispute Resolution Services
- Business Support
C. Article to share:
In a survey of a total of 877 university undergraduates in Hong Kong. Five reasons to do an internship:
- gaining a better understanding of the workplace culture (51.9%);
- creating a more attractive resume (51.0%)
- applying knowledge in an actual work context (44.7%)
- exploring career development (44%)
- learning beyond the classroom
November 2022 Hong Kong Report
Employment:
Hong Kong’s unemployment rate drops to 4.1%
Looking for Talents
Over the past two years, the local workforce shrank by about 140 000.
- launch the Top Talent Pass Scheme for a period of two years.
- Eligible talents will include individuals whose annual salary reached HK$2.5 million or above in the past year, and
- individuals graduated from the world’s top 100 universities with at least three years of work experience over the past five years.


- Individuals who graduated from the world’s top 100 universities in the past five years and have yet to fulfil the work experience requirement will also be eligible, subject to an annual quota of 10 000. The scheme will be reviewed after the first year of implementation;
- These two categories of talents will be issued a two-year pass for exploring opportunities in Hong Kong and are not subject to any quota.
Career development workshop
- Activity: Career planning & industry sharing
- Date: 20 September 2022
- Participants: around 130 secondary school students


August 2022 Hong Kong Report
- Confirmed case per day: around 4500 cases
- Population with 1st dose: 93.0%
- Population with 2nd dose: 89.6%
- Population with 3rd dose: 67.6%
B. Employment market
Hong Kong’s latest unemployment rate dropped to 5.1 percent as the city’s labor minister expected the market to further improve following relaxed Covid curbs and distribution of the second HK$5,000 consumption voucher.
C. Employment Situation of Graduates of Full-time UGC-funded Programmes by Level of Study, 2020/21
D. Other
A local enterprise piloted 4.5-Day Work Week This Summer
Some companies allowed their employees to work from home 1 or 2 days per week
February 2022 Hong Kong Report
Overview
- Population: 7394.7 (Mid-year 2021 number ‘000)
- Unemployment rate: 3.9 (10/2021 – 12/2021)
- GDP: +4.8 (Q4 2021)
COVID
- Population with 1st Vaccine Dose: 5,348,686 (79.4%)
- Population with 2nd Vaccine Dose: 4,810,574 (71.4%)
- Population with 3rd Vaccine Dose: 954,018
- Population Aged 5-11 with 1st Vaccine Dose: 12,302(3.0%)
- Confirmed cases: 13,829
- Hospitalized: 1,103
- Death:213
Geography
- Hong Kong is situated at the south-eastern tip of the mainland of China, with a total area of about
- 1 110.2 square kilometres covering Hong Kong Island, Kowloon, and the New Territories and Islands.
Land area of Hong Kong
| Sq. km (as of Year 2020) | |
|---|---|
| Hong Kong Island | 80.7 |
| New Territories and Islands | 982.5 |
| Total | 1 110.2 |
Population
| – | Year 2020 | – |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Number (‘000) | % |
| Male | 3 416.3 | 47.5 |
| Female | 4 065.5 | 54.3 |
| Total | 7 481.8 | 100.0 |
Mid-year population by age group
| – | Year 2020 | – |
|---|---|---|
| Age Group | Number (‘000) | % |
| Under 15 | 869.3 | 11.6 |
| 15 – 34 | 1 690.2 | 22.6 |
| 35 – 64 | 3 550.5 | 47.5 |
| 35 – 64 | 3 550.5 | 47.5 |
| 65 and over | 31 371.8 | 18.3 |
| Total | 7 481.8 | 100.0 |
Labour force by age group
| – | Year 2020 | – |
|---|---|---|
| Age Group | Number (‘000) | % |
| Under 15 | 240 | 6.2 |
| 15 – 34 | 1 876 | 48.2 |
| 35 – 64 | 1 614 | 47.5 |
| 35 – 64 | 3 550.5 | 4.1 |
| 65 and over | 158 | 18.3 |
| Total | 3 888 | 100.0 |
Distribution of Composite Employment Estimates by industry section
| Industry section | 2020 (%) |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 2.2 |
| Electricity and gas supply | 2.2 |
| Water supply; sewerage, waste management and remediation services | 2.3 |
| Construction | 8.4 |
| Wholesale | 1.4 |
| Import and export trade | 10.5 |
| Retail | 7.8 |
| Transportation, storage, postal and courier services | 7.8 |
| Accommodationand food services | 6.4 |
| Information and communications | 3.1 |
| Financing and insurance | 7.6 |
| Administrative and support services | 5.4 |
| Public administration | 3.3 |
| Education | 6.0 |
| Human health and social work services | 5.9 |
| Arts, entertainment and recreation | 1.4 |
| Other social and personal services | 12.6 |
| Other | 0.1 |
| All industry sections | 100.0 |
| Total employment (‘000)s | 3 653.8 |
Note :
(1) – University Grants Committee-funded universities
(2) – publicly-funded institution
Statistics on Students of Programmes Funded through the University Grants Committee
According to the information of the Census and Statistics Department, the proportion of Hong Kong population who have attained higher education continues to increase over the years. By 2018, nearly a quarter of the population aged 15 and over was educated to first degree level or above.
The University Grants Committee (UGC) is a non-statutory body which advises the Government of the Special Administrative Region on the funding and strategic development of higher education in Hong Kong. This article presents and analyses the statistics on university students of programmes funded through the UGC after the implementation of the New Academic Structure from 2012/13 academic year.
The UGC, established in 1965, advises the Government on the funding allocation to its funded universities and offers impartial and respected expert advice to the Government on the strategic development of higher education in Hong Kong. The Administration and the UGC adopt a triennial planning cycle in determining the recurrent funding for the UGC-funded sector, which provides the much needed certainty of funding over a three-year period. For each triennium, the UGC engages in a substantive process of discussion with the universities on their Planning Exercise Proposals (PEPs) and student number targets. Subject to a predetermined Cash Limit from the Administration for the entire sector, the UGC will then make triennial funding recommendations for the 8 UGC-funded universities to the Chief Executive, reflecting the indicative student number targets and the approved PEPs as settled with the universities. The recommendations, after deliberated upon within the Administration, will be put to the LegCo Panel on Education for consultation, and to the Finance Committee for endorsement of the financial implications.
At present, there are 8 universities in Hong Kong funded through the UGC:
- City University of Hong Kong https://www.cityu.edu.hk/
- Hong Kong Baptist University https://www.hkbu.edu.hk/eng/main/index.jsp
- Lingnan University https://www.ln.edu.hk/
- The Chinese University of Hong Kong https://www.cuhk.edu.hk/chinese/index.html
- The Education University of Hong Kong https://www.eduhk.hk/en/
- The Hong Kong Polytechnic University https://www.polyu.edu.hk/en/
- The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology https://hkust.edu.hk/home
- The University of Hong Kong https://www.hku.hk/
Institutions
- Caritas Institute of Higher Education https://www.cihe.edu.hk/en/home/index.html
- Centennial College https://www.centennialcollege.hku.hk/
- Chu Hai College of Higher Education https://www.chuhai.edu.hk/eng/index.html
- City University of Hong Kong (1) https://www.cityu.edu.hk/
- Gratia Christian College http://www.gcc.edu.hk/
- HKCT Institute of Higher Education https://www.hkct.edu.hk/en
- Hong Kong Academy for Performing Arts (2) https://www.hkapa.edu/
- Hong Kong Baptist University (1) https://www.hkbu.edu.hk/eng/main/index.jsp
- Hong Kong Metropolitan University https://www.hkmu.edu.hk/
- Hong Kong Nang Yan College of Higher Education http://www.ny.edu.hk/web/eng/home.html
- Hong Kong Shue Yan University https://www.hksyu.edu/en/
- Lingnan University (1) https://www.ln.edu.hk/
- Technological and Higher Education Institute of Hong Kong, Vocational Training Council https://www.thei.edu.hk/
- The Chinese University of Hong Kong (1) https://www.cuhk.edu.hk/chinese/index.html
- The Education University of Hong Kong (1) https://www.eduhk.hk/en/
- The Hang Seng University of Hong Kong https://www.hsu.edu.hk/en/
- The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (1) https://www.polyu.edu.hk/
- The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (1) https://hkust.edu.hk/
- The University of Hong Kong (1) https://www.hku.hk/
- Tung Wah College https://www.twc.edu.hk/en/index.php
- UOW College Hong Kong https://www.cccu.edu.hk/home.html
- Yew Chung College of Early Childhood Education https://www.yccece.edu.hk/en/
Secondary School Education
- provide 12 years’ free primary and secondary education to all children through public sector schools. In addition, the Government provides full subvention for full-time courses run by the Vocational Training Council for Secondary 3 leavers to offer an alternative free avenue for senior secondary students outside mainstream education;
- provide a balanced and diversified school education that suits the different needs of students to enable them to develop knowledge, positive values and attitudes as well as generic skills and become responsible citizens, and to prepare them for further studies or work to make contributions to Hong Kong and the nation;
- enable students to become proficient in biliterate and trilingual communication;
- enhance teaching quality and effectiveness in learning;
- improve the learning and teaching environment;
- provide students with special educational needs (SEN) with education services to develop their potentials to the full;
- help newly-arrived children (including newly-arrived children from the Mainland, non-Chinese speaking children and returnee children) integrate into the local community and overcome learning difficulties; and
- enhance the quality, flexibility and accountability of school administration.

